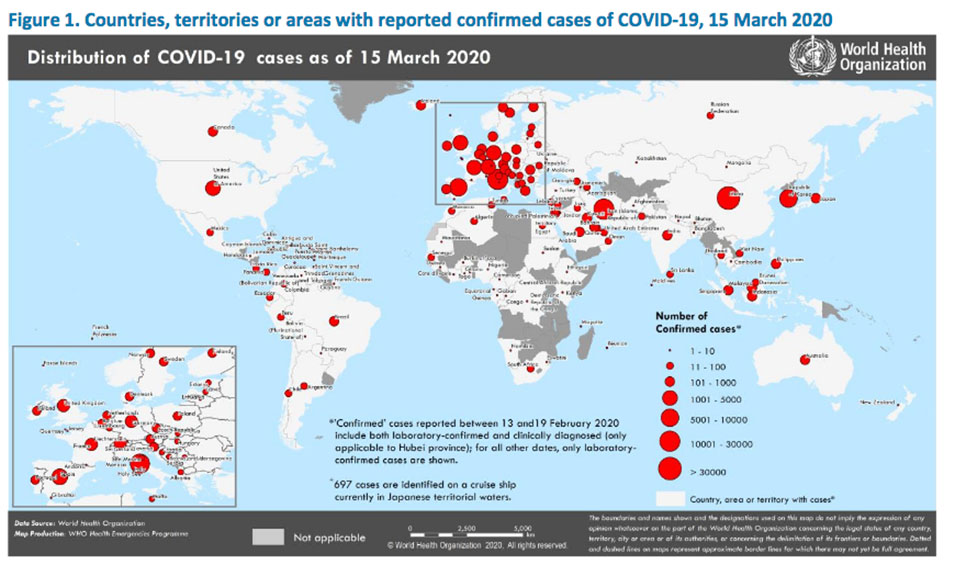
The World Health Organization reported last night that COVID-19 had reached nine new countries/territories/areas, seven in the African Region, one in the European Region and one in the Region of Americas, during the previous 24 hours..
According to the WHO situation report on March 15 (CET) COVID-19 now is in 144 countries/territories and areas (although many of those are only 1 or 2 imported cases of people with COVID-19.)
Globally, 153,517 cases have been confirmed, 10,982 are new cases. There have been 5735 deaths, and 343 new deaths since the last WHO Situation Report of 14 March.

The WHO website answers some frequently asked questions:
What is a Coronavirus?
Coronaviruses are a large family of viruses which may cause illness in animals or humans. In humans, several coronaviruses are known to cause respiratory infections ranging from the common cold to more severe diseases such as Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) and Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS). The most recently discovered coronavirus causes coronavirus disease COVID-19.
What is COVID-19?
COVID-19 is the infectious disease caused by the most recently discovered coronavirus. This new virus and disease were unknown before the outbreak began in Wuhan, China, in December 2019.
What are the symptoms of COVID-19?
The most common symptoms of COVID-19 are fever, tiredness, and dry cough. Some patients may have aches and pains, nasal congestion, runny nose, sore throat or diarrhea. These symptoms are usually mild and begin gradually. Some people become infected but don’t develop any symptoms and don't feel unwell. Most people (about 80%) recover from the disease without needing special treatment. Around 1 out of every 6 people who gets COVID-19 becomes seriously ill and develops difficulty breathing. Older people, and those with underlying medical problems like high blood pressure, heart problems or diabetes, are more likely to develop serious illness. People with fever, cough and difficulty breathing should seek medical attention.
How does COVID-19 spread?
People can catch COVID-19 from others who have the virus. The disease can spread from person to person through small droplets from the nose or mouth which are spread when a person with COVID-19 coughs or exhales. These droplets land on objects and surfaces around the person. Other people then catch COVID-19 by touching these objects or surfaces, then touching their eyes, nose or mouth. People can also catch COVID-19 if they breathe in droplets from a person with COVID-19 who coughs out or exhales droplets. This is why it is important to stay more than 1 meter (3 feet) away from a person who is sick.
WHO is assessing ongoing research on the ways COVID-19 is spread and will continue to share updated findings.
Can the virus that causes COVID-19 be transmitted through the air?
Studies to date suggest that the virus that causes COVID-19 is mainly transmitted through contact with respiratory droplets rather than through the air. See previous answer on “How does COVID-19 spread?”
You can reduce your chances of being infected or spreading COVID-19 by taking some simple precautions:
- Regularly and thoroughly clean your hands with an alcohol-based hand rub or wash them with soap and water.
- Washing your hands with soap and water or using alcohol-based hand rub kills viruses that may be on your hands.
- Maintain at least 1 metre (3 feet) distance between yourself and anyone who is coughing or sneezing.
- When someone coughs or sneezes they spray small liquid droplets from their nose or mouth which may contain virus. If you are too close, you can breathe in the droplets, including the COVID-19 virus if the person coughing has the disease.
- Avoid touching eyes, nose and mouth.
- Hands touch many surfaces and can pick up viruses. Once contaminated, hands can transfer the virus to your eyes, nose or mouth. From there, the virus can enter your body and can make you sick.
- Make sure you, and the people around you, follow good respiratory hygiene. This means covering your mouth and nose with your bent elbow or tissue when you cough or sneeze. Then dispose of the used tissue immediately.
- Why? Droplets spread virus. By following good respiratory hygiene you protect the people around you from viruses such as cold, flu and COVID-19.
- Stay home if you feel unwell. If you have a fever, cough and difficulty breathing, seek medical attention and call in advance. Follow the directions of your local health authority.
Is it safe to receive a package from any area where COVID-19 has been reported?
Yes. The likelihood of an infected person contaminating commercial goods is low and the risk of catching the virus that causes COVID-19 from a package that has been moved, travelled, and exposed to different conditions and temperature is also low.
Is there anything I should not do?
The following measures ARE NOT effective against COVID-2019 and can be harmful:
- Smoking
- Wearing multiple masks
- Taking antibiotics
- In any case, if you have fever, cough and difficulty breathing seek medical care early to reduce the risk of developing a more severe infection and be sure to share your recent travel history with your health care provider.
Are antibiotics effective in preventing or treating the COVID-19?
No. Antibiotics do not work against viruses, they only work on bacterial infections. COVID-19 is caused by a virus, so antibiotics do not work. Antibiotics should not be used as a means of prevention or treatment of COVID-19. They should only be used as directed by a physician to treat a bacterial infection.
Can I catch COVID-10 from my pet?
While there has been one instance of a dog being infected in Hong Kong, to date, there is no evidence that a dog, cat or any pet can transmit COVID-19. COVID-19 is mainly spread through droplets produced when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or speaks. To protect yourself, clean your hands frequently and thoroughly.
WHO continues to monitor the latest research on this and other COVID-19 topics and will update as new findings are available.
How likely am I do catch COVID-19?
The risk depends on where you are - and more specifically, whether there is a COVID-19 outbreak unfolding there.
For most people in most locations the risk of catching COVID-19 is still low. However, there are now places around the world (cities or areas) where the disease is spreading. For people living in, or visiting, these areas the risk of catching COVID-19 is higher. Governments and health authorities are taking vigorous action every time a new case of COVID-19 is identified. Be sure to comply with any local restrictions on travel, movement or large gatherings. Cooperating with disease control efforts will reduce your risk of catching or spreading COVID-19.
COVID-19 outbreaks can be contained and transmission stopped, as has been shown in China and some other countries. Unfortunately, new outbreaks can emerge rapidly. It’s important to be aware of the situation where you are or intend to go. WHO publishes daily updates on the COVID-19 situation worldwide.
Are there any medicines or therapies that can prevent or cure COVID-19?
While some western, traditional or home remedies may provide comfort and alleviate symptoms of COVID-19, there is no evidence that current medicine can prevent or cure the disease. WHO does not recommend self-medication with any medicines, including antibiotics, as a prevention or cure for COVID-19. However, there are several ongoing clinical trials that include both western and traditional medicines. WHO will continue to provide updated information as soon as clinical findings are available.